Node.js Events
Node.js Events
When we say about the Node.js Events, in Node.js application events and callbacks are the concepts which are used to provide concurrency. Node.js applications are single threaded and every API of the Node.js are basicaly asynchronous. So to main concurrency here we uses async function. And node uses observer pattern. And Node.js thread keeps an event loop and after the completion of any tasks, it fires the corresponding event which will signals the event listener function to get executed.
Node.js Event Driven Programming
Well, Node.js uses event driven programming. Which means as soon as Node.js starts its server, this will simply initiates its variables, declares functions and then simply waits for event to occur. And this is one of the main reason that's why Node.js is pretty fast compared to other similar technologies.
There is a main loop in the event driven application which listens for events, and then triggers a callback function when of one of those events is detected.
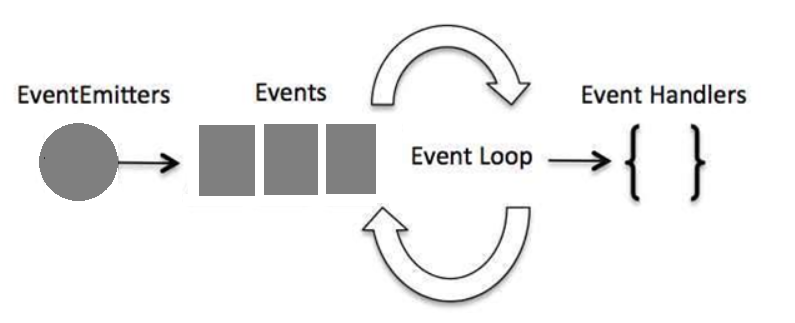
Difference between Events and Callbacks:
We will define some most important difference in between Events and Callbacks. Although, Events and Callbacks look similar but the differenences lies in fact that callback functions are mainly called when an asynchronous function returns it result where as event handling works on the observer pattern. And whenever any of event get fired, which means listener function starts executing. Node.js has multiple in-built events available through events module and EventEmitter class which is used to bind events and event listeners.
EventEmitter class to bind event and event listener:
//Here we import events module
var events = require('events');
//Here we create an eventEmitter object
var eventEmitter = new events.EventEmitter();
To bind event handler with an event:
// Bind event and even handler as follows
eventEmitter.on('eventName', eventHandler);
To fire an event:
To bind event handler with an event:
// Fire an event
eventEmitter.emit('eventName');
Node.js Event Example
File: main.js
// Import events module
var events = require('events');
// Create an eventEmitter object
var eventEmitter = new events.EventEmitter();
// Create an event handler as follows
var connectHandler = function connected() {
console.log('connection succesful.');
// Fire the data_received event
eventEmitter.emit('data_received');
}
// Bind the connection event with the handler
eventEmitter.on('connection', connectHandler);
// Bind the data_received event with the anonymous function
eventEmitter.on('data_received', function(){
console.log('data received succesfully.');
});
// Fire the connection event
eventEmitter.emit('connection');
console.log("Program Ended.");
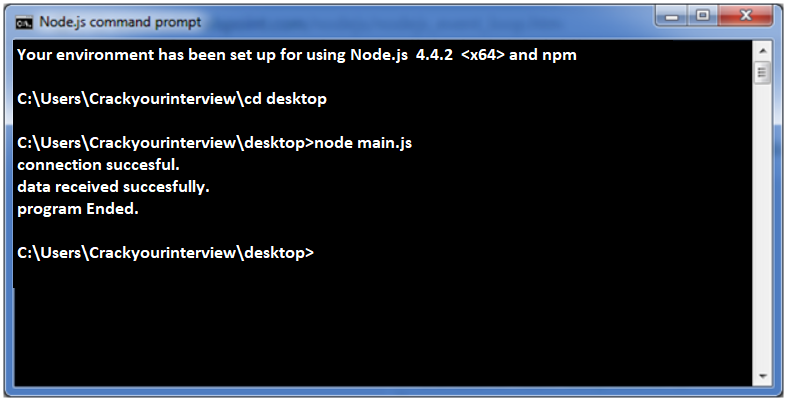
Now we open the Node.js command prompt and run the below code:
node main.js